Our full research programme currently consists of over 20 projects, some of which our delivered solely in-house but where possible we work in collaboration with other research partners. This increases the knowledge and expertise available, links us to other work and ensures increased return on our investment. The work within each pillar varies dependent on which issues have most importance or urgency to the industry.
BBRO Research
Prof. Mark Stevens
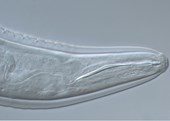
Crop Protection, virus and disease
Crop Stability is focused on delivering a clean, consistent and healthy crop which will maximize the yield potential from the genetics and growing environment. We know the potential of the existing genetics and aim to close the current gap between actual and potential yield. The need to ensure we have alternative strategies for the loss of active ingredients and the impact of government legislation changes such as neonicotinoid loss are paramount to the success of the crop.
Crop Stability is focused on delivering a clean, consistent and healthy crop which will maximize the yield potential from the genetics and growing environment. We know the potential of the existing genetics and aim to close the current gap between actual and potential yield. The need to ensure we have alternative strategies for the loss of active ingredients and the impact of government legislation changes such as neonicotinoid loss are paramount to the success of the crop.
Early detection of disease and variety variation are key components of our programme.
Current: Stewardship to support the use of Cruiser SB seed
The EU ban on neonicotinoids in 2018 fundamentally impacted the industry, with the subsequent use of Thiamethoxam treated seed only available under a Defra dero...
Current: Varietal susceptibility to virus yellows
Info to follow - Goliath, Verde and Titan trials
Current: IPM tools to combat virus yellows
The Virus Yellows Complex is the greatest threat to sustainable sugar beet production in North-West Europe. Since the removal of Neonicotinoids from use in 2018...
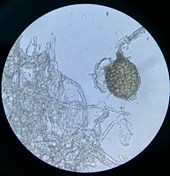
Current: BCN Screening
Info to follow
Current: Annual broad-leaved weed control in sugar beet
The project will look at economic and feasible options for annual broad-leaved weed (ABLW) control in sugar beet in the absence of triflusulfuron-methyl (TSM) o...
Current: Review of models and data for use in a Virus yellows Decision Support System
Virus yellows (VY) is the most important insect-related issue in UK sugar beet production. VY is a complex of aphid vectored viruses, which includes Beet mild y...
Current: Cercospora SporeNet & isolate monitoring
Cercospora Leaf Spot (CLS), caused by the fungus Cercospora beticola, can cause significant yield losses (up to 50%) in sugar beet crops around the globe. In th...
Current: Beet Moth: strategies to monitor and control
The beet moth (Scrobipalpa ocellatella) is not usually regarded as a serious pest in the UK or NW Europe. However, in 2022, favoured by the hot dry summer, the ...
Current: Supporting new IPM decisions using virus yellows model (StatBeet)
This project will combine statistical analysis and both stochastic and simulation modelling approaches applied to a wealth of data (i.e. from: BBRO experiments ...
Current: ABCD of Aphid IPM
The virus yellows complex (VY) in sugar beet can result in severe yield losses, as witnessed in the 2020 epidemic in the UK sugar beet crop. 38.1% of the crop w...
Current: Managing insecticide resistance
This is a new project linked to previous work with Rothamsted and a number of partners relating to insecticide resistance. Monitoring for resistance or reduc...
Current: AphidNet: automatic aphid recognition and counting based on field water trap imagery by deep learning
This work is extremely timely as the UK 2020 aphid/virus situation has been unprecedented, following the exceptionally mild January and February (reflected in t...
Current: Integrated disease control in sugar beet
The most important fungal foliar diseases affecting sugar beet in the UK have historically been rust (Uromyces betae) and powdery mildew (Erysiphe betae), both ...
Current: Development of crop management strategies for ‘free-living’ plant parasitic nematodes infecting sugar beet (Beta vulgaris)
Plant parasitic nematodes (PPNs) are important pests for many crops globally and result in a c. 14% loss of production annually, which equates £132 billion. The...
Current: Investigating the physiological effect of fungicides on sugar beet
The use of fungicides in sugar beet has become commonplace in the past 10-15 years with the majority of crops now receiving two sprays per year, and late harves...
Current: Validating guidance for insecticide resistance management across commodities
Guidance for the management of insecticide resistance has long advocated that:
Current: Mature plant resistance
The project focuses on the phenomenon of mature plant resistance (MPR) to control the spread and impact of yellowing viruses of sugar beet. MPR is a general def...
Current: Virus yellows forecasting
Infection by beet yellowing viruses causes a significant risk to sugar beet yields. Beet yellowing viruses comprise Beet Yellows Virus (BYV), Beet Mild Yellowin...
Current: Variety interaction with Virus Yellows
This project will provide information to determine whether any current/future RL varieties respond differently to virus yellows infection (BMYV and BYV) and hen...
Current: Virus yellows: aphid monitoring and alternative control strategies using existing/novel insecticides
Virus yellows is a greater problem in the UK than anywhere else in Europe due to the influence of our maritime climate. Virus threats are accentuated by the ong...
Complete: Effects of sodium and triazole fungicides on yield and quality on soils of different K index
Sugar beet take up and utilise large quantities of potassium (K) and sodium (Na) - uptakes of 300-400 kg K/ha and over 100 kg Na/ha are common. Potassium and ...
Complete: Insecticide resistance dynamics in aphid vectors of beet viruses
Sugar beet yellows is a disease caused by three viruses, Beet mild yellowing virus (BMYV), Beet chlorosis virus (BChV) and Beet yellows virus (BYV). BMYV and BC...
Complete: Agronomic strategies and the economics of organic beet production
Arable cropping has been shown to be economically and technically viable under organic management (Cormack, 1999). However, in the late 1990s, despite strong gr...
Complete: Control of late season foliar diseases
In recent years, a significant proportion of the growth of the beet crop has taken place during the late summer and autumn and it has therefore become increasin...
Complete: Weed Control Review: Desk study
ADAS were contracted to review current weed control options and future opportunities for UK crops.
Complete: Spray Application Review: Desk study
Research into optimum spray application methods for controlling weeds, pests and diseases for sugar beet has been very limited in the UK and there is scope for ...
Closed: Innovative strategies to control and monitor sugar beet pests and diseases
This project integrates closely with existing BBRO and BBSRC LINK- supported projects on disease resistance, foliar disease control and nematode dynamics.
Complete: Interactions between beet cyst nematode, sugar beet and brassica crops
BCN poses a serious threat to growers who cultivate sugar beet on infested fields. This project supersedes: Beet Cyst nematode: control and rotational issue...
Complete: Population genetics and ecology of a leaf mining pest
Climate change is causing changes in the nature and distribution of crop pest and disease populations, resulting in novel threats to food security. Biological r...
Complete: Innovate UK: A novel pre-breeding strategy to reduce dependence on insecticides for virus yellows control in sugar beet
Virus yellows is a major economic disease affecting sugar beet; its impact is particularly significant in the UK due to our maritime climate, and will be exacer...
Closed: Innovate UK: Innovative disease monitoring and diagnostics for improved efficiency of crop production (SPOREID)
SPOREID is a new project designed to minimise the impact of disease on yield of the UK sugar beet crop. The yield potential of the UK sugar beet crop is c.130 t...
Closed: Monitoring the future risk of rhizomania
Previously, rhizomania had a major economic impact on the UK industry, potentially decreasing yields by up to 70%. The development of partially-resistant variet...
Complete: Discovering the source of sugar beet infection and re-infection by rust and powdery mildew
Powdery mildew and rust can cause sugar yield losses of up to 20% and 14% respectively. Little is known about (1) the level of diversity of E. betae races, (2) ...
Closed: Predicting egg hatch in mangold fly (leaf miner)
The larvae of the mangold fly (Pegomya hyoscyami) mine extensively sugar beet leaves, resulting in blisters that reduce photosynthetic area, increase sensitivit...
Complete: Maximising sugar yield via fungicides
Previous fungicide trials have shown that the application of a single fungicide can give yield benefits of up to 8 adjusted t/ha and, from a two-spray strategy,...
Closed: Beet cyst nematode: control and rotational issues with brassica species
The significance and importance of oilseed rape and other brassica species in sugar beet rotations is increasing. An appreciation of these rotational issues and...
Complete: Combating resistance to aphicides in UK aphid pests
Supported by the Chemical Regulation Directorate (CRD), and a consortium of agrochemical companies and levy boards, this project provides research on aphicide r...
Complete: Mitigating new threats from virus yellows: monitoring aphid populations and insecticide resistance to maintain control
To optimise and sustain the use of insecticides on beet by providing forecasts and up-to-date information on the timing and abundance of aphids, their virus con...
Overseen by Dr Vicky Foster - Head of BBRO
Soil, Water, Nutrition
The crop production research programme is targeted at areas where we believe there is the greatest potential for development.
The programme focuses on closing the yield gap between the commercial crop and the variety trials. Whilst improved genetics have had high impact there is a need to strengthen our understanding in other key areas such as:
- soil management
- early crop rooting and canopy development
- how the crop is influenced by environmental relationships; water, nutrients, soil and temperature.
The crop progression research programme is targeted at areas where we believe there is the greatest potential for development.
The programme focusses on closing the yield gap between the commercial crop and the variety trials. Whilst improved genetics have had high impact there is a need to strengthen our understanding in other key areas such as:
- soil management
- early crop rooting and canopy development
- how the crop is influenced by environmental relationships; water, nutrients, soil and temperature.
It is well known that there is a direct relationship between radiation interception and sugar yield so the key to producing a high yield crop is early canopy closure which enables the crop to utilise the higher levels of solar radiation received in June and July.
Aspects of agronomy such as soil management & cultivation, variety choice, plant population, planting dates, the nutritional and water requirement of our crops are therefore important factors in influencing the progression of our yields.
Current: Identifying low carbon nitrogen fertilisers that are compatible with the demands of sugar beet production
Reducing the amount of fertiliser used on the sugar beet crop is the first stage of reducing emissions. The second stage is to change the fertiliser product bei...
Current: Optimizing nitrogen application to sugar beet using placement and banding of fertiliser
Nitrogen fertiliser is the one of the biggest sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions on farm from the sugar beet crop. Calculations from a report commissione...
Current: BetaSoils
A multi-faceted project to investigate how to optimise practices to maximise soil health.
Current: Optimising sugar beet management practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
With an industry target to reach net zero in agriculture by 2040 it is imperative that emissions are quantified and addressed on farm. Currently this is driven ...
Current: Assessing drought tolerance in UK sugar beet varieties
On average 59% of the fields in which sugar beet is grown consist of soil which is classified as sand based (loamy sand, sand, sandy clay loam, sandy loam, sand...
Current: The evaluation of new seed treatments, priming technologies and/or pellet types for the UK sugar beet market
BBRO protocol for evaluating new seed treatments, priming technologies and/or pellet types for the UK
Current: Canopy Architecture
This project is focusing on sugar beet radiation use efficiency (RUE) which is examining radiation (sunlight) interception by the canopy and measuring its resul...
Current: AHDB Soil Biology and Soil Health
BBRO are pleased to support this large industry collaboration on soil biology and health.
Current: Variety Trials Programme
The Recommended List Trials Programme involves approx.17 sites, of which up to 13 are taken for yield assessments. The programme includes trials for disease ass...
Closed: Optimising plant populations and N rates for modern, high-yielding sugar beet crops
There is circumstantial evidence to suggest that some UK high yielding sugar beet crops grown under modern conditions may benefit from higher than recommended p...
Closed: Intra-field Variation
Interpreting and managing the spatial heterogeneity in sugar beet yields by long-term monitoring of crops. INSPiRE (Interpreting & managing spatial performance...
Closed: Minimisation of sugar yield due to frost
Freezing temperatures can damage sugar beet roots, often leading to losses in sugar and causing problems during processing . Better understanding of the environ...
Closed: Nitrogen Prediction Response Evaluation (NPRE)
The fertiliser recommendations for sugar beet as laid out by DEFRA in RB209 assume a yield of 60t/ha. Whilst there is no evidence that higher yielding crops req...
Complete: Comparison of soil and foliar applied nutrition to improve yields
A number of approaches to ensure developing seedling receive optimum nutrition are practiced across a range of other crops. This includes: seed-applied nutritio...
Closed: Sequential Variety Harvest
Investigation into the relationship between variety canopy growth characteristics and the yield performance of sugar beet varieties at different harvest dates a...
Complete: The role of agronomy and genotype in tissue integrity and associated sugar losses during storage.
Average losses in clamp are approximately 0.1% of total sugar volume per day (BBRO, 2016). These losses are a consequence of many factors including harvesting ...
Closed: Assessment of the reduction of sugar losses by adopting a direct transfer 'Chaser'-based harvesting system
The use of chaser bins (also known as transfer wagons) are not an entirely new concept and have been used widely in Australia and North America transferring gra...
Closed:To investigate UK sugar beet cleaner loader losses
The harvester testing program has highlighted instances of both good and bad whole beet losses through cleaner loaders (often the same make/model) highlighting ...
Closed: Beet plant spatial layout -equidistant plant spacing
Work done in the 1900s (SBREC) demonstrated that drilling beet on a 30x30cm grid delivered increased sugar yields of 4-5%. The challenge of precision drilling ...
Complete: Analysis of the causes of recent changes in beet amino-N and alkalinity
Since the mid 1990s, the average concentration of amino-N in beet delivered to British Sugar factories has decreased progressively from around 160 to 70mg/100g/...
Complete: Benchmarking grower’s production to the potential yield set by the environment
The aim of this project was to provide growers with a tool to analyse their past performance so that they can separate the effects of differences between season...
Complete: Chemical blocking of seed set in weed beet
Weed beet is an increasing problem in the UK, and current methods to keep populations in check are laborious, expensive, and often ineffective. If the productio...
Complete: Factors influencing crown size and the implications for crown tare
The crown tares of delivered beet have large financial implications for both grower and processor. Their lower concentrations of sugar and higher concentration...
Complete: Using multi-environment variety trial data to screen for drought tolerance
Insufficient moisture during summer months limits UK sugar beet production more than any other single factor. Compared with potential production without stress,...
Complete: Early-sown bolting trials to characterise varietal bolting
The BBRO vernalization-intensity bolting model for sugar beet - initially reported in the final report of an earlier BBRO Project and published in its final ve...
Complete: Economics of sugar beet irrigation in England
The experimental (field) data on the response of sugar beet to irrigation in England was reviewed. The literature mostly dates from the 1970s and 1980s and show...
Complete: Enhanced biodiversity in SB rotations
A crucial part of the year for birds is winter, when resources are low, and survival difficult. Inclusion of a spring-sown crop such as sugar beet, predominantl...
Complete: Evaluation of novel defoliators
To evaluate the yield gains that could be obtained in commercial sugar beet defoliation systems.
Complete: Genetic influences of sugar beet cell wall composition on biorefining
Aim: to understand the genetic basis of variation in sugar beet cell wall composition.
Complete: Genotypic differences in susceptibility to frost damage
Temperatures during the 2010/11 campaign caused significant levels of frost damage to beet still in the ground, resulting in major financial losses to growers a...
Complete: Selection methods for the improvement of drought tolerance and water use efficiency in sugar beet
In 2006, 27 genotypes were tested under irrigated and managed drought conditions using the polytunnel system. These genotypes consisted of six ‘core’ hybrids th...
Complete: Inputs / outputs
Effects of increased input costs on crop profitability
Complete: Factory estimates of K in beet tissue water for monitoring the potassium status of soils
The project used beet and soil sampled by British Sugar staff from individual fields prior to the 2005-06 processing campaign to validate the use of factory tar...
Complete: Mind the gap
In England, sugar beet must compete with wheat and oilseed-rape for a place in the arable rotation. At today’s prices for wheat (c. £160/t) and beet (c. £26/t)...
Complete: Maximising the benefits from cover crops through species selection and crop management (Maxi-Cover Crop)
This project aims to maximise the potential economic, agronomic and ecological benefits from cover crops through a better understanding of species effects and c...
Complete: Maximizing deliveries of freshly-lifted beet throughout an extended harvesting campaign
The UK sugar-beet industry needs to improve the cost-effectiveness of sugar production if it is to remain competitive within the new EU Sugar Regime. This may r...
Complete: Performance evaluation of precision sugar beet drills
This evaluation tested seven drills at two speeds and on two soil types. Drill performance was measured by uniformity of seed spacing. There was variability in ...
Complete: Monitoring sugar beet storage
The project will re-evaluate sugar losses during storage to take account of modern 'whole beet' recovery practices and the increasing use of A-shaped storage cl...
Complete: The effect of paper pulp on the beet crop
Landfill is becoming increasingly expensive. This project assessed the impact of the use of paper pulp on sugar beet .
Complete: Placed nitrogen phosphate
This project will show whether, by placing N, can we improve N uptake efficiency and improve the performance of crops and to what extent it may be possible to r...
Complete: Post-harvest storage losses of different varieties in clamp and consequences of triazole usage
In a two-year project conducted by British Sugar plc, clamps were constructed at two sites, using beet grown on a sandy loam and clay loam soils. Storage loss...
Complete: Plant populations and N rate
Assessment of the impact of increased plant populations and N rates on high-fertility soils
Complete: Review of strip tillage for sugar beet beet production
The objective to this proposed project is to produce a review to better understand how strip tillage is currently being used in sugar beet in the United Kingdom...
Complete: Safe methods of applying protective sheeting to beet clamps
To design, develop and provide a commercial alternative system that allows sugar beet clamps to be covered for protection against frost and uncovered after a fr...
Complete: Development of strip tillage techniques in sugar beet production
Strip tillage is a non-inversion technique that has been widely adopted in some areas of the United States for growing row crops e.g. maize and sugar beet. This...
Complete: Seed rates for the new sugar regime
The last experiments on the effects of plant population density on the performance of UK sugar-beet crops on which much of our current advice is based were done...
Complete: Sugar beet response to additional applications of sulphur fertiliser and the identification of soil & cropping systems
Work on other arable crops such as OSR and cereals has shown that crops frequently respond to additional sulphur fertilisers, especially on lighter land where t...
Complete: Varietal differences in crown size and greater recovery of crown material at harvest
The UK sugar-beet industry has largely achieved its objective of increasing national average yields to 70 t/ha. The opportunities offered by recovering and proc...
Complete: To increase the profitability and sustainability of the UK sugar beet industry through reductions in soil tare
Large quantities of soil adhering to beet are delivered to factories during the campaign at considerable cost to the industry in transportation, removal and dis...
Complete: The effect of cover crops on soil structure and the subsequent sugar beet yield
The project is investigating the effect of autumn/winter cover crops on the physical structure of soil before and throughout the sugar beet crop and how this ma...
Complete: Understanding soil plant interactions to improve sugar beet productivity
On average, 10% of sugar beet yield is lost to drought in the UK. In field surveys are being used to identify constraints to rooting at depth, which limits wate...
Complete: Sulphur fertiliser for sugar beet
Like nitrogen, sulphur is an essential ingredient in proteins, and what little evidence there is suggests that healthy beet crops should contain 25-35 kg/ha (Ho...
Complete: Synchronised Granule Application
This project examined the efficacy of synchronised application of a nematicide granule compared to a continuous band application at drilling for the control of...
Complete: Value of sugar beet crop for birds and farm environment
This project examined bird use of sugar beet crops in summer and autumn. Foraging and breeding behaviour, along with data on plant food and vegetation composit...
Complete: Understanding water use efficiency in sugar beet
This project focuses on water use efficiency (WUE) in sugar beet, which examines the plant’s water use and the associated yields achieved. Sugar beet is often o...
Complete: Understanding the genetic determinants of dry matter composition
To understand the key genetic factors influencing the composition and development of the cell wall in sugar beet roots.
Complete: Understanding water uptake in sugar beet
It has been long known that sugar beet does not yield well under drought conditions. In the UK there is a 10% yield loss as a result of drought on average and i...
Complete: Consideration of the supply of beet for biofuel production
The EU proposes that a significant proportion of transport fuel shall come from renewable resources.